Nori Porcine S100A4 ELISA Kit
$461.00 – $832.00
DataSheet CoA SDS
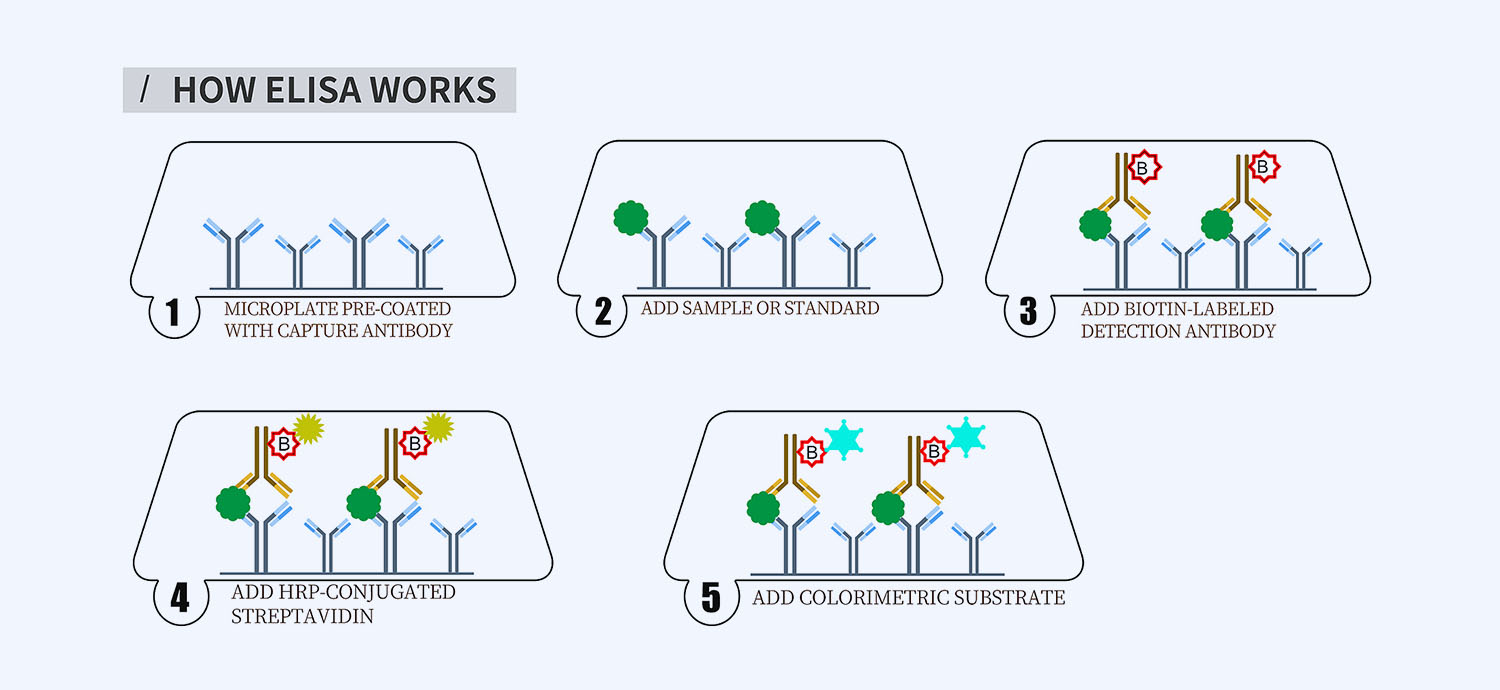
This ELISA kit is for quantification of S100A4 in pig. This is a quick ELISA assay that reduces time to 50% compared to the conventional method, and the entire assay only takes 3 hours. This assay employs the quantitative sandwich enzyme immunoassay technique and uses biotin-streptavidin chemistry to improve the performance of the assays. An antibody specific for S100A4 has been pre-coated onto a microplate. Standards and samples are pipetted into the wells and any S100A4 present is bound by the immobilized antibody. After washing away any unbound substances, a detection antibody specific for S100A4 is added to the wells. Following wash to remove any unbound antibody reagent, a detection reagent is added. After intensive wash a substrate solution is added to the wells and color develops in proportion to the amount of S100A4 bound in the initial step. The color development is stopped, and the intensity of the color is measured.
Alternative names for S100A4: S100 calcium-binding protein A4, S100-A4
This product is for laboratory research use only not for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes or any other purposes.
- Description
- How Elisa Works
- Product Citation (0)
- Reviews (0)
Description
Nori Porcine S100A4 ELISA Kit Summary
Alternative names for S100A4: S100 calcium-binding protein A4, S100-A4
Alternative name for porcine: Pig
| Assay Type | Solid Phase Sandwich ELISA |
| Format | 96-well Microplate or 96-Well Strip Microplate |
| Method of Detection | Colorimetric |
| Number of Targets Detected | 1 |
| Target Antigen Accession Number | F1SFV7 |
| Assay Length | 3 hours |
| Quantitative/Semiquantitative | Quantitative |
| Sample Type | Plasma, Serum, Cell Culture, Urine, Cell/Tissue Lysates, Synovial Fluid, BAL, |
| Recommended Sample Dilution (Plasma/Serum) | No dilution for sample <ULOQ; sufficient dilution for samples >ULOQ |
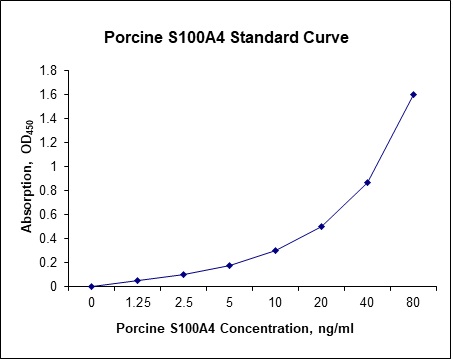
| Sensitivity | 250 pg/mL |
| Detection Range | 1.25-80 ng/mL |
| Specificity | Natural and recombinant porcine S100A4 |
| Cross-Reactivity | < 0.5% cross-reactivity observed with available related molecules, < 50% cross-species reactivity observed with species tested. |
| Interference | No significant interference observed with available related molecules |
| Storage/Stability | 4 ºC for up to 6 months |
| Usage | For Laboratory Research Use Only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic use. |
| Additional Notes | The kit allows for use in multiple experiments. |
Standard Curve
Kit Components
1. Pre-coated 96-well Microplate
2. Biotinylated Detection Antibody
3. Streptavidin-HRP Conjugate
4. Lyophilized Standards
5. TMB One-Step Substrate
6. Stop Solution
7. 20 x PBS
8. Assay Buffer
Other Materials Required but not Provided:
1. Microplate Reader capable of measuring absorption at 450 nm
2. Log-log graph paper or computer and software for ELISA data analysis
3. Precision pipettes (1-1000 µl)
4. Multi-channel pipettes (300 µl)
5. Distilled or deionized water
Protocol Outline
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards as instructed in the datasheet.
2. Add 100 µl of Standard or samples to each well and incubate 1 h at RT.
3. Add 100 µl of Working Detection Antibody to each well and incubate 1 h at RT.
4. Add 100 µl of Working Streptavidin-HRP to each well and incubate 20 min at RT.
5. Add 100 µl of Substrate to each well and incubate 5-30 min at RT.
6. Add 50 µl of Stop Solution to each well and read at 450 nm immediately.
Background:
S100 calcium-binding protein A4 (S100A4) is a protein that is encoded by the S100A4 gene.[1] S100A4 is a member of the S100 family of proteins containing 2 EF-hand calcium-binding motifs. S100 proteins are localized in the cytoplasm and/or nucleus of a wide range of cells, and involved in the regulation of a number of cellular processes such as cell cycle progression and differentiation. S100A4 may function in motility, invasion, and tubulin polymerization. Altered expression of S100A4 have been implicated in tumor metastasis. S100A4 is secreted by tumor and stromal cells, supports tumorigenesis by stimulating angiogenesis. Research demonstrated that S100A4 synergizes with VEGF via the RAGE receptor, in promoting endothelial cell migration by increasing KDR expression and MMP-9 activity. In vivo overexpression of S100A4 led to a significant increase in tumor growth and vascularization in a Porcine melanoma xenograft M21 model. Conversely, when silencing S100A4 by shRNA technology, a dramatic decrease in tumor development of the pancreatic MIA PaCa-2 cell line was observed. S100A4 is highly associated with components of the cytoskeleton and when this gene is upregulated, it changes the cell’s morphology, making it more susceptible to invasion from proteins, such as cathepsin B and cyclin B1, that contribute to metastasis.[2] Together, these factors form polyploid giant cancer cells (PGCCs), which are highly proliferative and invasive. Experimental knockout therapy data have suggested that S100A4 exhibits a form of control over cathepsin B and cyclin B1, and that suppressing it can reduce the invasive capabilities of PGCCs and their daughter cells. Studies on invasive breast cancer have found that S100A4 plays a major role in high-density collagen deposition, which is one of the clinical symptoms of tumor metastasis. Significantly higher levels of S100A4 were found in samples that exhibited lymph node metastasis than in those that didn’t, indicating that abnormal collagen deposition could be contributed by S100A4.[3] Not only does overexpression of S100A4 contribute to the formation of various cancers, but it also contributes to pathological factors associated with cancer and its progression.
References
- Stoler A, Bouck N (1985). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82 (2): 570–4.
- Fei F, Liu K, Li C, et al. (2020) Front Oncol. 10:182.
- Wen X, Yu X, Tian Y, et al. (2020) Quant Imaging Med Surg. 10(3):624-633.






















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.