Nori Human VCAM-1 ELISA Kit
$461.00 – $832.00
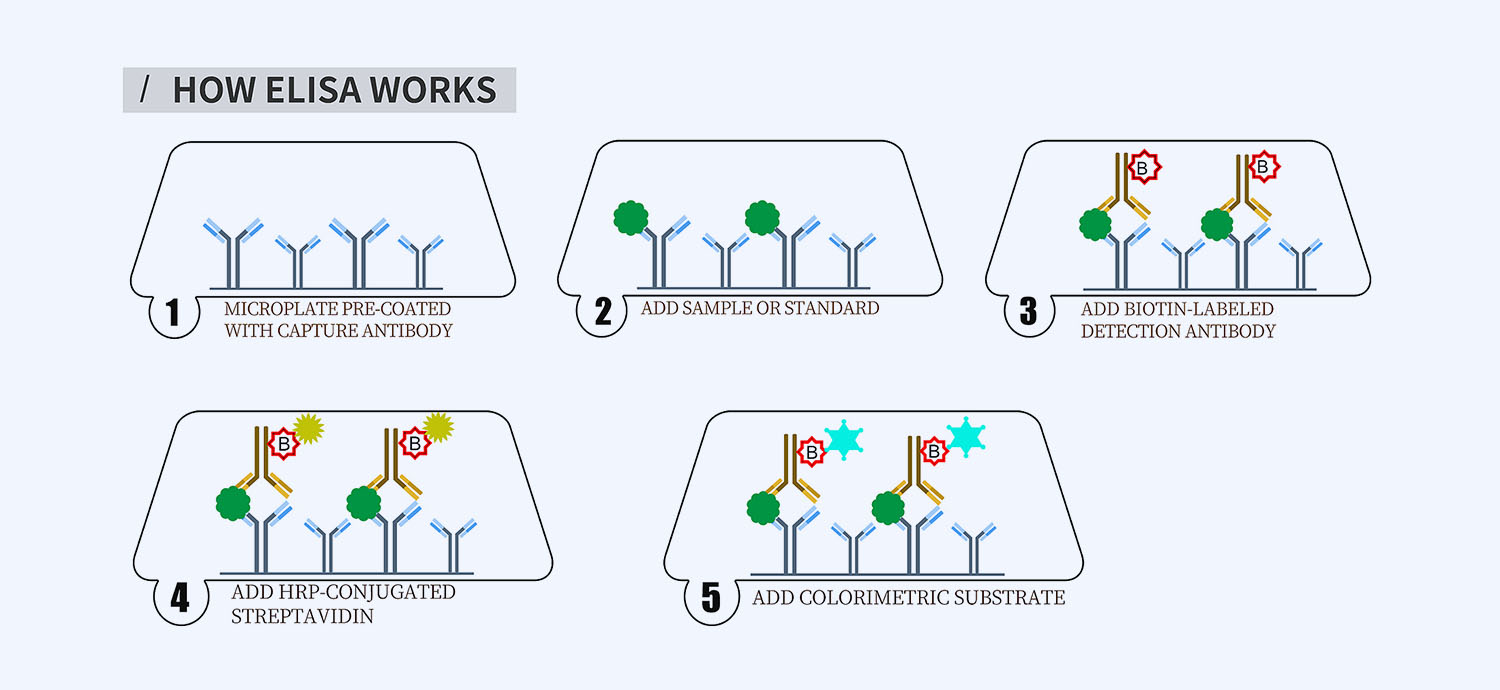
This ELISA kit is for quantification of VCAM-1 in human. This is a quick ELISA assay that reduces time to 50% compared to the conventional method, and the entire assay only takes 3 hours. This assay employs the quantitative sandwich enzyme immunoassay technique and uses biotin-streptavidin chemistry to improve the performance of the assays. An antibody specific for VCAM-1 has been pre-coated onto a microplate. Standards and samples are pipetted into the wells and any VCAM-1 present is bound by the immobilized antibody. After washing away any unbound substances, a detection antibody specific for VCAM-1 is added to the wells. Following wash to remove any unbound antibody reagent, a detection reagent is added. After intensive wash a substrate solution is added to the wells and color develops in proportion to the amount of VCAM-1 bound in the initial step. The color development is stopped, and the intensity of the color is measured.
Alternative names for VCAM-1: Vascular cell adhesion protein 1, vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1), cluster of differentiation 106 (CD106)
This product is for laboratory research use only, not for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes or any other purposes.
- Description
- How Elisa Works
- Product Citations
- Reviews (0)
Description
Nori Human VCAM-1 ELISA Kit Summary
Alternative names for VCAM-1: Vascular cell adhesion protein 1, vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1), cluster of differentiation 106 (CD106)
| Assay Type | Solid Phase Sandwich ELISA |
| Format | 96-well Microplate or 96-Well Strip Microplate |
| Method of Detection | Colorimetric |
| Number of Targets Detected | 1 |
| Target Antigen Accession Number | P19320 |
| Assay Length | 3 hours |
| Quantitative/Semiquantitative | Quantitative |
| Sample Type | Plasma, Serum, Cell Culture, Urine, Cell/Tissue Lysates, Synovial Fluid, BAL, |
| Recommended Sample Dilution (Plasma/Serum) | No dilution for sample <ULOQ; sufficient dilution for samples >ULOQ |
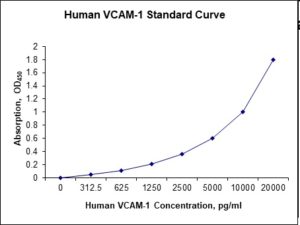
| Sensitivity | 60 pg/mL |
| Detection Range | 0.312-20 ng/mL |
| Specificity | Human VCAM-1 |
| Cross-Reactivity | < 0.5% cross-reactivity observed with available related molecules, < 50% cross-species reactivity observed with species tested. |
| Interference | No significant interference observed with available related molecules |
| Storage/Stability | 4 ºC for up to 6 months |
| Usage | For Laboratory Research Use Only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic use. |
| Additional Notes | The kit allows for use in multiple experiments. |
Standard Curve
Kit Components
1. Pre-coated 96-well Microplate
2. Biotinylated Detection Antibody
3. Streptavidin-HRP Conjugate
4. Lyophilized Standards
5. TMB One-Step Substrate
6. Stop Solution
7. 20 x PBS
8. Assay Buffer
Other Materials Required but not Provided:
1. Microplate Reader capable of measuring absorption at 450 nm
2. Log-log graph paper or computer and software for ELISA data analysis
3. Precision pipettes (1-1000 µl)
4. Multi-channel pipettes (300 µl)
5. Distilled or deionized water
Protocol Outline
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards as instructed in the datasheet.
2. Add 100 µl of Standard or samples to each well and incubate 1 h at RT.
3. Add 100 µl of Working Detection Antibody to each well and incubate 1 h at RT.
4. Add 100 µl of Working Streptavidin-HRP to each well and incubate 20 min at RT.
5. Add 100 µl of Substrate to each well and incubate 5-30 min at RT.
6. Add 50 µl of Stop Solution to each well and read at 450 nm immediately.
Background:
Vascular cell adhesion protein 1 also known as vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1) or cluster of differentiation 106 (CD106) is a protein that is encoded by the VCAM1 gene.[1] The VCAM-1 mediates the adhesion of lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils to vascular endothelium. It functions in leukocyte-endothelial cell signal transduction, and it may play a role in the development of atherosclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis. Upregulation of VCAM-1 in endothelial cells by cytokines occurs as a result of increased gene transcription (e.g., in response to TNF-α and Interleukin-1 and through stabilization of mRNA for cytokine genes (e.g., IL-4). The promoter region of the VCAM-1 gene contains functional tandem NF-κB sites. The sustained expression of VCAM-1 lasts over 24 hours. VCAM-1 is an endothelial ligand for VLA-4 of the β1 subfamily of integrins. VCAM-1 expression has also been observed in other cell types (e.g., smooth muscle cells). It interacts with EZR and Moesin.[2] VCAM-1 also exists on the surface of some subpopulations of mesenchymal stem cells(MSC).[3]
Certain melanoma cells can use VCAM-1 to adhere to the endothelium,[4] VCAM-1 may participate in monocyte recruitment to atherosclerotic sites, and it is highly overexpressed in the inflamed brain.[5]
References
- Cybulsky M, et al. (1991). “The human VCAM1 gene is assigned to chromosome 1p31-p32”. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 58 (3–4): 1850–1867.
- Barreiro O, et al. (2002). “Dynamic interaction of VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 with moesin and ezrin in a novel endothelial docking structure for adherent leukocytes”. J. Cell Biol. 157 (7): 1233–45.
- ZX Yang; et al. (2013). “CD106 identifies a subpopulation of mesenchymal stem cells with unique immunomodulatory properties”. PLOS One. 8 (3): e59354.
- Eibl RH, Benoit M (2004). “Molecular resolution of cell adhesion forces”. IEE Proceedings – Nanobiotechnology. 151 (3): 128–32.
- Marcos-Contreras, Oscar A (2020). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 117 (7): 3405–3414.
























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.