Nori Human COX-2 ELISA Kit
$461.00 – $832.00
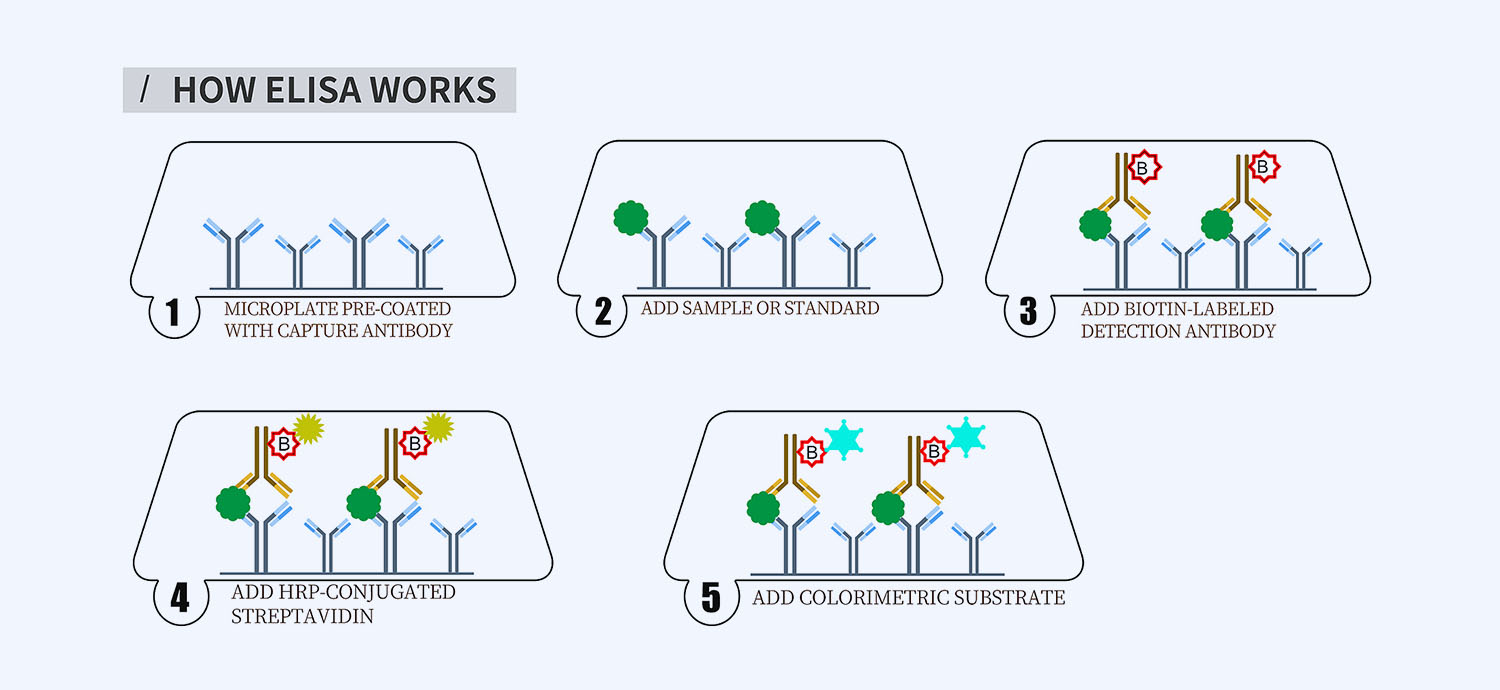
This ELISA kit is for quantification of COX-2 in human. This is a quick ELISA assay that reduces time to 50% compared to the conventional method, and the entire assay only takes 3 hours. This assay employs the quantitative sandwich enzyme immunoassay technique and uses biotin-streptavidin chemistry to improve the performance of the assays. An antibody specific for COX-2 has been pre-coated onto a microplate. Standards and samples are pipetted into the wells and any COX-2 present is bound by the immobilized antibody. After washing away any unbound substances, a detection antibody specific for COX-2 is added to the wells. Following wash to remove any unbound antibody reagent, a detection reagent is added. After intensive wash a substrate solution is added to the wells and color develops in proportion to the amount of COX-2 bound in the initial step. The color development is stopped, and the intensity of the color is measured.
Alternative names for COX-2: Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), Prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 (prostaglandin G/H synthase and cyclooxygenase), COX2
This product is for laboratory research use only, not for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes or any other purposes.
- Description
- How Elisa Works
- Product Citations
- Reviews (0)
Description
Nori Human COX-2 ELISA Kit Summary
Alternative names for COX-2: Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), Prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 (prostaglandin G/H synthase and cyclooxygenase), COX2
| Assay Type | Solid Phase Sandwich ELISA |
| Format | 96-well Microplate or 96-Well Strip Microplate |
| Method of Detection | Colorimetric |
| Number of Targets Detected | 1 |
| Target Antigen Accession Number | P00403 |
| Assay Length | 3 hours |
| Quantitative/Semiquantitative | Quantitative |
| Sample Type | Plasma, Serum, Cell Culture, Urine, Cell/Tissue Lysates, Synovial Fluid, BAL, |
| Recommended Sample Dilution (Plasma/Serum) | No dilution for sample <ULOQ; sufficient dilution for samples >ULOQ |
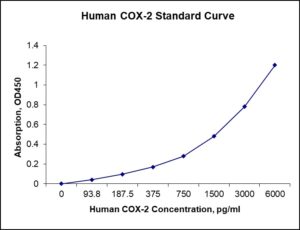
| Sensitivity | 18 pg/mL |
| Detection Range | 93.8-6000 pg/mL |
| Specificity | Human COX-2 |
| Cross-Reactivity | < 0.5% cross-reactivity observed with available related molecules, < 50% cross-species reactivity observed with species tested. |
| Interference | No significant interference observed with available related molecules |
| Storage/Stability | 4 ºC for up to 6 months |
| Usage | For Laboratory Research Use Only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic use. |
| Additional Notes | The kit allows for use in multiple experiments. |
Standard Curve
Kit Components
1. Pre-coated 96-well Microplate
2. Biotinylated Detection Antibody
3. Streptavidin-HRP Conjugate
4. Lyophilized Standards
5. TMB One-Step Substrate
6. Stop Solution
7. 20 x PBS
8. Assay Buffer
Other Materials Required but not Provided:
1. Microplate Reader capable of measuring absorption at 450 nm
2. Log-log graph paper or computer and software for ELISA data analysis
3. Precision pipettes (1-1000 µl)
4. Multi-channel pipettes (300 µl)
5. Distilled or deionized water
Protocol Outline
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards as instructed in the datasheet.
2. Add 100 µl of Standard or samples to each well and incubate 1 h at RT.
3. Add 100 µl of Working Detection Antibody to each well and incubate 1 h at RT.
4. Add 100 µl of Working Streptavidin-HRP to each well and incubate 20 min at RT.
5. Add 100 µl of Substrate to each well and incubate 5-30 min at RT.
6. Add 50 µl of Stop Solution to each well and read at 450 nm immediately.
Background:
Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), also known as Prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 (prostaglandin G/H synthase and cyclooxygenase), is an enzyme that in Felines is encoded by the PTGS2 gene.[1] It is involved in the conversion of arachidonic acid to prostaglandin H2, an important precursor of prostacyclin and thromboxane A2, among others. COX-2, converts arachidonic acid (AA) to prostaglandin endoperoxide H2. PTGS2 (COX-2) is unexpressed under normal conditions in most cells, but elevated levels are found during inflammation. PTGS1 (COX-1) is constitutively expressed in many tissues and is the predominant form in gastric mucosa and in the kidneys. Inhibition of PTGS1 (COX-1) reduces the basal production of cytoprotective PGE2 and PGI2 in the stomach, which may contribute to gastric ulceration. Since PTGS2 (COX-2) is generally expressed only in cells where prostaglandins are upregulated (e.g., during inflammation), drug-candidates that selectively inhibit PTGS2 (COX-2) were suspected to show fewer side-effects [2] but proved to substantially increase risk for cardiovascular events such as heart attack and stroke. Two different mechanisms may explain contradictory effects. Low-dose aspirin protects against heart attacks and strokes by blocking PTGS1 (COX-1) from forming a prostaglandin called thromboxane A2. It sticks platelets together and promotes clotting; inhibiting this helps prevent heart disease. On the other hand, PTGS2 (COX-2) is a more important source of prostaglandins, particularly prostacyclin which is found in blood vessel lining. The expression of PTGS2 (COX-2) is upregulated in many cancers. The overexpression of PTGS2 (COX-2) along with increased angiogenesis and SLC2A1 (GLUT-1) expression is significantly associated with gallbladder carcinomas.[3] Furthermore the product of PTGS2 (COX-2), PGH2 is converted by prostaglandin E2 synthaseinto PGE2, which in turn can stimulate cancer progression. Consequently inhibiting PTGS2 (COX-2) may have benefit in the prevention and treatment of these types of cancer.[4]
References
- Hla T, Neilson K (1992). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89 (16): 7384–8.
- Kurumbail RG, et al. (2001). Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 11 (6): 752–60.
- Legan M (2010). Bosn J Basic Med Sci 10 (3): 192–6.
- Menter DG, et al. (2010). Clin. Cancer Res. 16 (5): 1384–90.























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.