Nori Canine ApoB ELISA Kit
$461.00 – $832.00
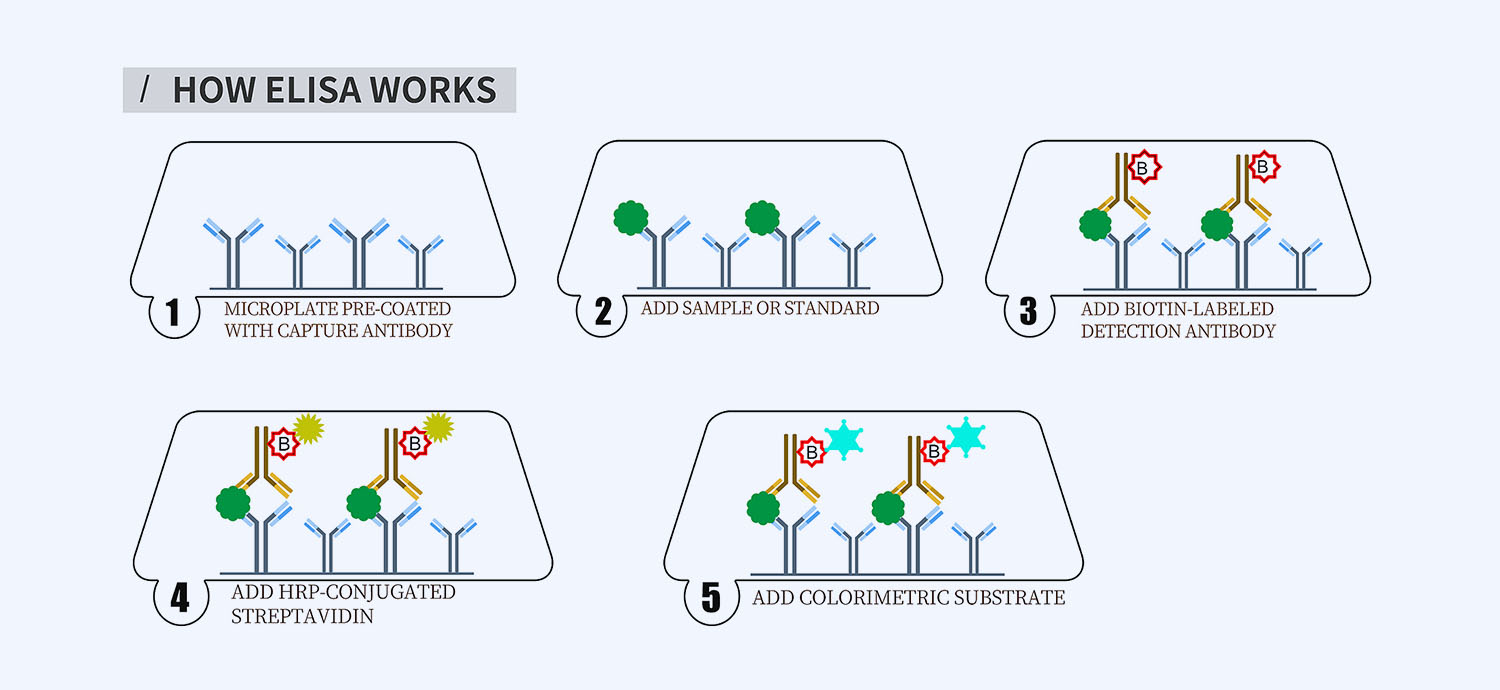
This ELISA kit is for quantification of ApoB in human. This is a quick ELISA assay that reduces time to 50% compared to the conventional method, and the entire assay only takes 3 hours. This assay employs the quantitative sandwich enzyme immunoassay technique and uses biotin-streptavidin chemistry to improve the performance of the assays. An antibody specific for ApoB has been pre-coated onto a microplate. Standards and samples are pipetted into the wells and any ApoB present is bound by the immobilized antibody. After washing away any unbound substances, a detection antibody specific for ApoB is added to the wells. Following wash to remove any unbound antibody reagent, a detection reagent is added. After intensive wash a substrate solution is added to the wells and color develops in proportion to the amount of ApoB bound in the initial step. The color development is stopped, and the intensity of the color is measured.
Alternative names for ApoB: Apolipoprotein B
This product is for Laboratory Research Use Only not for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes or any other purposes.
- Description
- How Elisa Works
- Product Citation (0)
- Reviews (0)
Description
Nori Canine Apob ELISA Kit Summary
Alternative names for ApoB: Apolipoprotein B
Alternative names for canine: Dog
| Assay Type | Solid Phase Sandwich ELISA |
| Format | 96-well Microplate or 96-Well Strip Microplate |
| Method of Detection | Colorimetric |
| Number of Targets Detected | 1 |
| Target Antigen Accession Number | A0A8I3S4D1 |
| Assay Length | 3 hours |
| Quantitative/Semiquantitative | Quantitative |
| Sample Type | Plasma, Serum, Cell Culture, Urine, Cell/Tissue Lysates, Synovial Fluid, BAL, |
| Recommended Sample Dilution (Plasma/Serum) | No dilution for sample <ULOQ; sufficient dilution for samples >ULOQ |
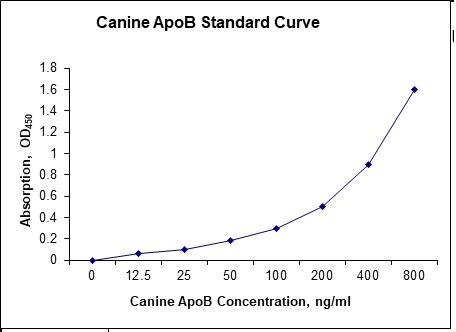
| Sensitivity | 2.5 ng/mL |
| Detection Range | 12.5-800 ng/mL |
| Specificity | Natural and recombinant canine ApoB |
| Cross-Reactivity | < 0.5% cross-reactivity observed with available related molecules, < 50% cross-species reactivity observed with species tested. |
| Interference | No significant interference observed with available related molecules |
| Storage/Stability | 4 ºC for up to 6 months |
| Usage | For Laboratory Research Use Only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic use. |
| Additional Notes | The kit allows for use in multiple experiments. |
Standard Curve
Kit Components
1. Pre-coated 96-well Microplate
2. Biotinylated Detection Antibody
3. Streptavidin-HRP Conjugate
4. Lyophilized Standards
5. TMB One-Step Substrate
6. Stop Solution
7. 20 x PBS
8. Assay Buffer
Other Materials Required but not Provided:
1. Microplate Reader capable of measuring absorption at 450 nm
2. Log-log graph paper or computer and software for ELISA data analysis
3. Precision pipettes (1-1000 µl)
4. Multi-channel pipettes (300 µl)
5. Distilled or deionized water
Protocol Outline
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards as instructed in the datasheet.
2. Add 100 µl of Standard or samples to each well and incubate 1 h at RT.
3. Add 100 µl of Working Detection Antibody to each well and incubate 1 h at RT.
4. Add 100 µl of Working Streptavidin-HRP to each well and incubate 20 min at RT.
5. Add 100 µl of Substrate to each well and incubate 5-30 min at RT.
6. Add 50 µl of Stop Solution to each well and read at 450 nm immediately.
Background:
Apolipoprotein B (ApoB) is a protein that in Canines is encoded by the APOB gene. ApoB is the primary apolipoprotein of chylomicrons, VLDL, IDL, and LDL particles, which is responsible for carrying lipids, including cholesterol, around the body to all cells within all tissues. ApoB is the primary organizing protein component of the particles and is absolutely required for the formation of these particles and the ApoB on the LDL particle acts as a ligand for LDL receptors in various cells throughout the body. High levels of ApoB are related to heart disease and are the primary driver of plaques that cause vascular disease (atherosclerosis), commonly first becoming obviously symptomatic as heart disease, stroke & many other body wide complications after decades of progression. There is considerable evidence that concentrations of ApoB[1] and especially the NMR assay[2] are superior indicators of vascular/heart disease driving physiology than either total cholesterol or LDL-cholesterol. ApoB occurs in the plasma in 2 main isoforms, ApoB48 and ApoB100. The first is synthesized exclusively by the small intestine, the second by the liver.[3] ApoB-100 is the largest of the apoB group of proteins, consisting of 4563 amino acids and both isoforms are coded by APOB.[3] ApoB48 is generated when a stop codon (UAA) at residue 2153 is created by RNA editing. Overproduction of apolipoprotein B can result in lipid-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and insulin resistance in the liver.[4] ApoB100 levels are associated with coronary heart disease, the number of ApoB100-containing lipoprotein particles which can carry lipids into the artery walls is a key determinant, driver of atherosclerosis and heart disease. The ApoB100 / ApoA1 ratio is more effective at predicting heart attack risk, in patients who had had an acute myocardial infarction, than either the ApoB100 or ApoA1 measure alone.[5] In the general population this remains unclear although in a recent study ApoB was the strongest risk marker for cardiovascular events.[6] ApoB has been shown to interact with apo(a), PPIB,[7] Calcitonin receptor[7] and HSP90B1.[7] Interaction of ApoB with proteoglycans, collagen, and fibronectin is believed to cause atherosclerosis.
References
- Lim JS, et al. (2011). Journal of Clinical Lipidology. 5 (4): 264–272.
- Carmena R, et al. (2004). Circulation. 109 (23): III–2.
- Chen SH, et al. (1986). Journal of Biological Chemistry. 261 (28): 12918–12921.
- Su Q, et al. (2009). Hepatology. 50 (1): 77–84.
- McQueen MJ, et al. (2008). Lancet. 372 (9634): 224–33.
- Benn M, et al. (2007). Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 27 (3): 661–70.
- Zhang J, Herscovitz H (2003). J. Biol. Chem. 278 (9): 7459–68.























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.